Table of Contents
Introduction
Emil Erlenmeyer’s life journey, from his humble beginnings to his enduring legacy in the world of chemistry, is a testament to the power of curiosity, dedication, and ingenuity.
Born on June 28, 1825, in Bavaria, Germany, Emil was the son of Johann Erlenmeyer, a respected pharmacist, and Maria Erlenmeyer.
Growing up in a household steeped in scientific inquiry and intellectual curiosity, Emil developed a keen interest in the natural world from an early age.
whose name is immortalized in the iconic laboratory equipment, the Erlenmeyer flask. However, his contributions to the field of chemistry extend far beyond this singular invention. Let’s delve into the life and works of this remarkable scientist.
Early Life and Education
Emil Erlenmeyer displayed an early aptitude for science and mathematics. He pursued his education with zeal, studying at various universities across Europe, including Heidelberg, Giessen, and Munich. His passion for chemistry blossomed under the tutelage of renowned scientists of his time
He studied under the guidance of renowned scientists such as Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wohler. Under their mentorship, Emil honed his skills as a chemist and embarked on a lifelong journey of discovery.
The Erlenmeyer Flask: A Symbol of Innovation
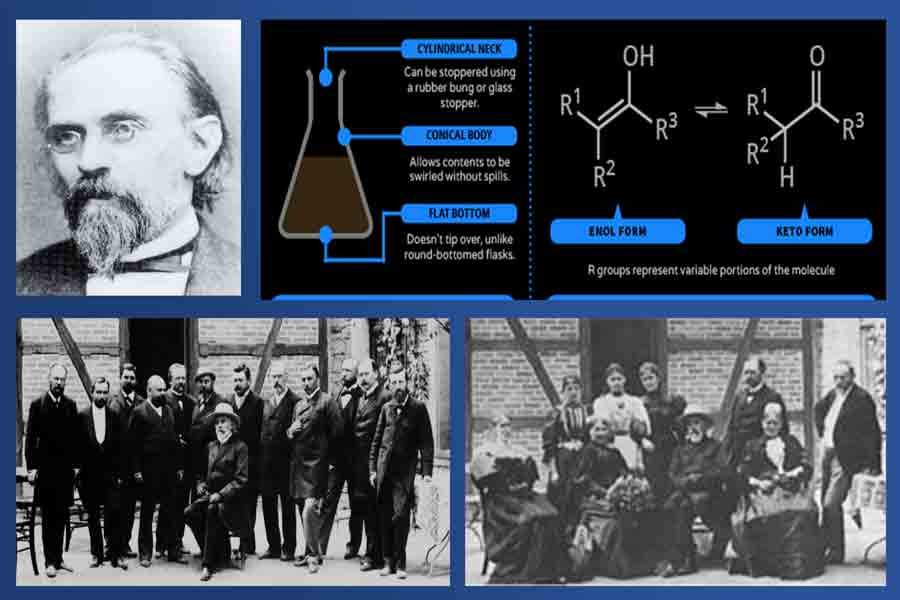
Erlenmeyer’s most enduring legacy is undoubtedly the conical flask that bears his name. In 1861, he introduced this revolutionary piece of laboratory glassware, characterized by its conical shape with a narrow neck. This design offers several advantages over traditional flat-bottomed flasks, including easier swirling of liquids, reduced risk of spills, and more efficient heat transfer.
The Erlenmeyer flask quickly gained popularity among chemists and remains an indispensable tool in laboratories worldwide. Its versatility extends beyond the simple containment of liquids; chemists employ it in various processes, from titrations to culturing microorganisms.
Contributions to Organic Chemistry
While the Erlenmeyer flask is Emil Erlenmeyer’s most famous invention, his contributions to organic chemistry are equally significant. He conducted pioneering research in several areas, including the synthesis of organic compounds and the study of chemical reactions.
One of Erlenmeyer’s notable achievements was his work on the synthesis of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. His synthetic methods laid the groundwork for future research in biochemistry and paved the way for advancements in pharmaceuticals.
His innovative synthetic methods paved the way for the development of new drugs and therapies, saving countless lives and improving human health and biotechnology.
Erlenmeyer’s Laws: A Legacy of Insight
In addition to his experimental work, Emil Erlenmeyer made significant contributions to theoretical chemistry. He formulated several laws that bear his name, elucidating fundamental principles governing chemical reactions and equilibrium.
Erlenmeyer’s laws encompass a range of phenomena, from the behavior of gases to the solubility of substances in solution. His meticulous experiments and insightful observations provided valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of chemical processes, earning him recognition as a leading figure in theoretical and chemistry experiments.
Meticulous Experiments:
In the ever-evolving realm of science, experiments are the bedrock upon which knowledge is built. The term “meticulous experiments” refers to the careful and precise design, execution, and analysis of experiments. These experiments stand up to scrutiny, yield reproducible results, and push the boundaries of our understanding. In this blog post, we delve into the importance of meticulous experiments, the elements that comprise them, and how they contribute to the broader scientific enterprise.
The Importance of Being Meticulous
Science thrives on accuracy and reliability. The meticulous nature of an experiment ensures that the findings are credible and can be trusted. This meticulousness is not just about avoiding errors; it’s about ensuring that every aspect of the experiment is thoughtfully considered. From the hypothesis formulation to the final analysis of the data, attention to detail is paramount. This thorough approach helps eliminate biases, reduce errors, and increase the results’ validity.
Key Elements of Meticulous Experiments
1. Clear Hypotheses and Objectives:
A meticulous experiment begins with a well-defined hypothesis and clear objectives. These guide the experimental design and provide a benchmark against which the results can be measured. The hypothesis should be specific, testable, and based on existing knowledge.
2. Detailed Experimental Design:
The design of an experiment is its blueprint. This includes selecting the appropriate variables, controls, and samples. Every step should be planned to ensure that the experiment can be replicated and the results can be compared. Consideration of potential confounding factors and how to mitigate them is a crucial part of this phase.
3. Accurate Data Collection:
Precision in data collection cannot be overstated. This involves using reliable tools and methods to gather data, ensuring consistency, and maintaining detailed records. Any deviations or anomalies should be documented and accounted for.
Although he published primarily scientific articles,
He also wrote several books.
Here are some notable ones:
- “Lehrbuch der organischen Chemie” (Textbook of Organic Chemistry): This comprehensive textbook is one of Erlenmeyer’s significant contributions to the field, covering various aspects of organic chemistry.
- “Zur Geschichte der Glykole und ihrer Derivate” (History of Glycols and Their Derivatives) This book deals with the chemistry and history of glycols, a class of organic compounds.
- “Über das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung freier organischer Radikale” (On the Occurrence and Significance of Free Organic Radicals) This work explores the importance of free radicals in organic chemistry.
Erlenmeyer’s work appears mainly in academic journals and collections of scientific articles rather than as stand-alone books. He published extensively in journals such as “Liebigs Annalen der Chemie” (Liebig’s Annals of Chemistry).
Quotes from Emil Erlenmeyer
Emil Erlenmeyer was a brilliant scientist and a profound thinker, whose words continue to resonate with scientists and scholars worldwide. Some of his notable quotes include:
“The pursuit of knowledge is the noblest endeavor of the human mind.”
“In chemistry, as in life, precision and clarity are essential for success.”
“Every experiment, no matter how small, holds the potential for discovery.”
“Curiosity is the spark that ignites the flame of discovery.”
Legacy and Influence
Emil Erlenmeyer died on January 22, 1909, aged 73. The exact cause of his death is not widely documented, and there is limited information about the circumstances surrounding his demise.
He may have died of natural causes or disease, but specific details of his death are not readily accessible in public records. Erlenmeyer’s contributions to chemistry, including the invention of the flask that bears his name, have left a lasting legacy in the scientific community.
Emil Erlenmeyer’s legacy extends far beyond his lifetime. His pioneering work in chemistry continues It should inspire generations of scientists, from students in classrooms to researchers in laboratories. The Erlenmeyer flask is a symbol of innovation and scientific inquiry, expressing Emile’s passion.
Extracurricular activity of Emil Erlenmeyer
Emil Erlenmeyer, known for the Erlenmeyer flask, was a prominent German chemist whose primary focus was on his scientific work. Although specific details of his extracurricular activities are not widely documented, some aspects of his life and interests beyond his direct scientific contributions can be inferred:
- Academic Involvement: Erlenmeyer was deeply involved in academia, not only as a researcher but also as a teacher. His commitment to education and mentoring students is seen as an extension of his professional work and personal interest in sharing knowledge.
- Scientific Societies: Like many scientists of his time, Erlenmeyer may have been involved in various scientific societies and professional organizations. These groups held frequent meetings, lectures, and discussions, providing opportunities for networking, collaboration, and staying updated with the latest scientific developments.
- Writing and Publishing: Erlenmeyer was an active writer and contributor to scientific literature. His extracurricular activities included writing dissertations and essays and corresponding with other scientists of his era.
- Family and Personal Life: Emil Erlenmeyer had a family; although specific details are scarce, it can be assumed that he spent time with his family. Balancing a difficult life with family life must have been an important part of his personal pursuits.
- Intellectual Interests: Given his profound influence on chemistry, it is plausible that Erlenmeyer had a wide range of interests in a variety of intellectual pursuits. These include attending lectures or seminars on developments in other scientific fields and participating in intellectual salons or debates common in 19th-century academic circles.
- Nature and Exploration: Many scientists of Erlenmeyer’s time were involved in nature and exploration. Erlenmeyer may have engaged in activities such as hiking, botanical study, or other forms of exploring the natural world, whether through travel related to his work or personal interest.
Although Emil Erlenmeyer’s specific extracurricular activities are not well documented, his career as a scientist and educator suggests a deep engagement with intellectual, educational, and possibly nature-related activities beyond his laboratory work
He likes Music
Specific details about Emil Erlenmeyer’s personal tastes in music are not well documented. However, given the time period in which he lived (1825–1909), it is possible to make some educated guesses about the types of music he might have been exposed to and possibly enjoyed:
- Classical Music: The 19th century was a golden age for classical music, with composers such as Ludwig van Beethoven, Johannes Brahms, Franz Schubert, and Richard Wagner producing some of their greatest works during this period. As a cultured and educated man, Erlenmeyer might have appreciated classical music, which was a dominant cultural force in Germany at the time.
- Folk Music: Traditional German folk music was also popular during the 19th century. Erlenmeyer may have enjoyed folk songs and dances, which were an integral part of German cultural life.
- Salon Music: The 19th century also saw the rise of salon music, a genre intended for performance in the intimate setting of private salons. This included piano pieces, lieder (German art songs), and chamber music, which Erlenmeyer could have enjoyed in social gatherings or at home.
- Opera: Germany had a strong tradition of opera, with composers like Wagner and Carl Maria von Weber making significant contributions. Erlenmeyer might have attended opera performances, which were popular cultural events at the time.
Without specific historical records, it isn’t easy to pinpoint Erlenmeyer’s exact musical preferences, but he likely enjoyed a mix of classical, folk, and contemporary music of his era, reflecting the rich musical culture of 19th-century Germany.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Emil Erlenmeyer’s life and work exemplify the transformative power of science and the boundless potential of human intellect. From his early days as the son of a pharmacist to his groundbreaking discoveries in chemistry, Emil’s journey is a testament to his enduring quest for knowledge and understanding. As we reflect on his contributions, we are reminded of the importance of curiosity, perseverance, and imagination in the pursuit of scientific discovery……learn more